Optimization of process parameters for bio-oil synthesis from pine needles (Pinus roxburghii) using response surface methodologySandip Mandal, T. K. Bhattacharya, A. K. Verma, and Juma Haydary ICAR-Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering, Nabibagh, India
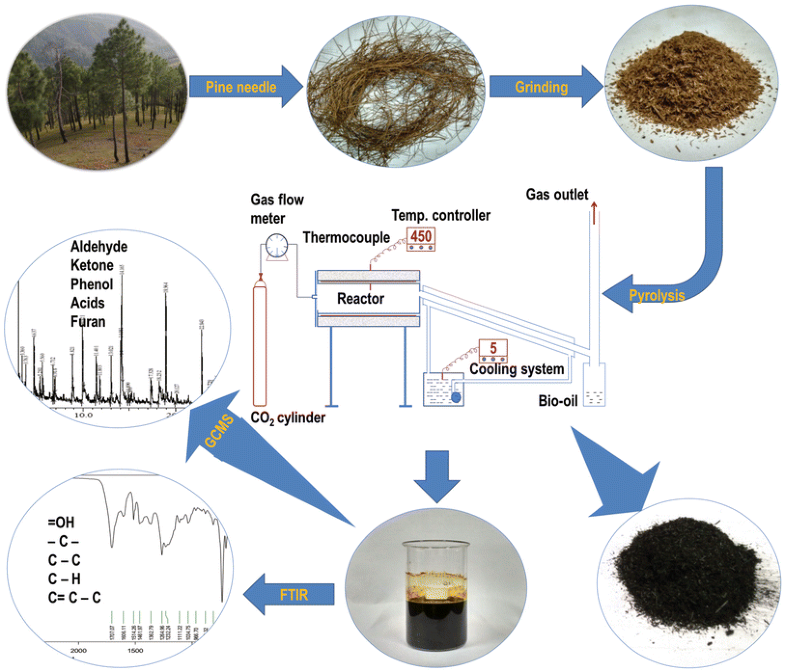
E-mail: sandip.mandal@icar.gov.in Abstract: Pine needles are the residue of pine (Pinus roxburghii) forest and a major cause of forest fire in the North Western hills of India. Experiments were conducted to convert pine needles into bio-oil and biochar through pyrolysis as an alternate way to use pine needles to reduce forest fire. Process parameters such as pyrolysis temperature, gas flow rate, vapor cooling temperature, heating rate were optimized by employing central composite design (CCD) in Response Surface Methodology (RSM). The maximum bio-oil yield was found at pyrolysis temperature of 547 °C, CO2 gas flow rate of 1.85 l min−1, vapor cooling temperature of 15 °C and heating rate of 50 °C min−1. Chemical characterization of bio-oil was conducted using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and gas chromatographic/mass spectroscopy (GC/MS). Fuel properties of bio-oil and biochar were determined using ASTM standard methods. The bio-oil recovered was found to be comparable with conventional liquid fuels in many aspects. The by-product, biochar, was found suitable as soil amendment as well as solid fuel with higher energy density than the pine needles.
Keywords: Pine needle ; Pyrolysis ; RSM ; Bio-oil ; Biochar Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-017-0306-5
Chemical Papers 72 (3) 603–616 (2018) |
Monday, June 02, 2025 |
|||
© 2025 Chemical Papers |
||||