A microporous metal–organic framework with soc topology for adsorption and separation selectivity of C2H2/CO2Xing Duan, Wei Zheng, Ben Yu, and Zhenguo Ji Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou, China
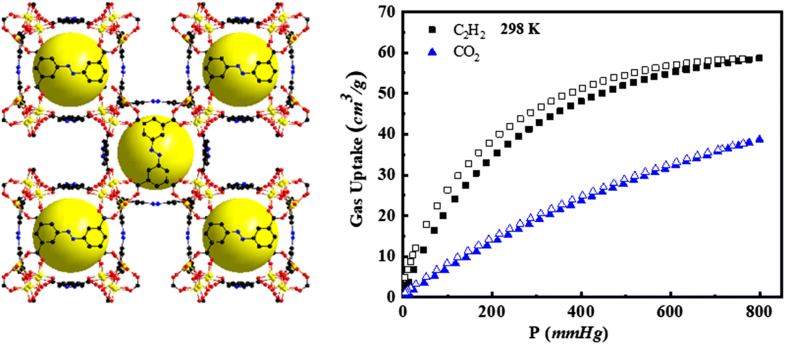
E-mail: star1987@hdu.edu.cn Abstract: The microporous metal–organic framework [Co3O(H2O)3](ABTC)1.5·(solv)x, (H4ABTC = 3,3′,5,5′-azobenzenetetracarboxylic acid) Co-ABTC, with suitable pore space was synthesized by solvothermal reaction. Co-ABTC shows the spherical pores with a radius of 5.2 × 5.2 Å2, taking into account the van der Waals’ force. The specific surface area (BET) is 585.9 m2/g through N2 adsorption at 77 K. The activated Co-ABTCa shows the moderately high separation selectivity for C2H2/CO2 of 4.28 (298 K) at extremely low pressures by utilizing ideal adsorbed solution theory simulation. A new microporous metal–organic framework with optimizing pore space has been realized to exhibit highly selective C2H2/CO2 gas separation property. Keywords: Metal–organic frameworks ; Adsorption ; Crystal structure ; Selective separation Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-019-00794-x
Chemical Papers 73 (9) 2371–2375 (2019) |
Thursday, April 03, 2025 |
|||
© 2025 Chemical Papers |
||||